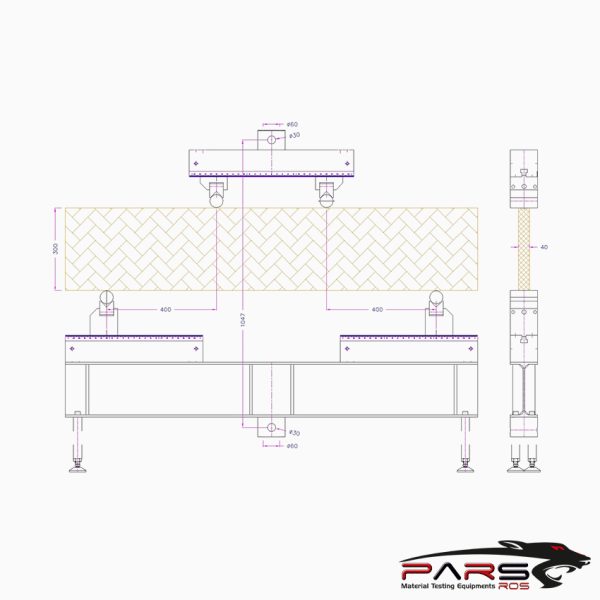
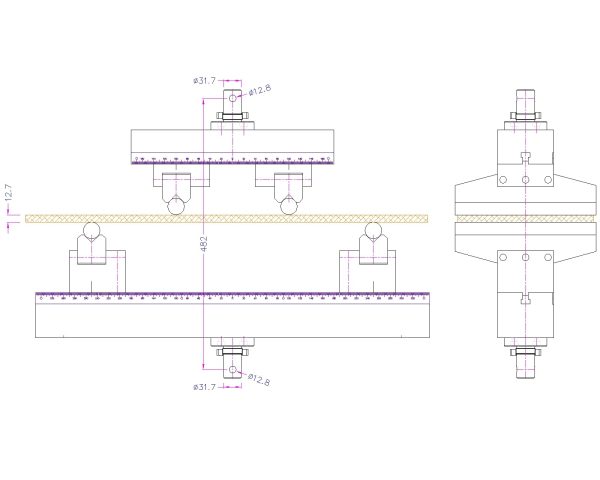
ASTM D6109 Test Fixture
ASTM D6109 – These test methods are suitable for determining the flexural properties for any solid or hollow manufactured plastic lumber product of square,
rectangular, round, or other geometric cross section that shows viscoelastic behavior.
Please Contact With Us For More Information
- Description
- Reviews (0)
- TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Description
Description
ASTM D6109 – Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastic Lumber and Related Products
ASTM D6109 – These test methods are suitable for determining the flexural properties for any solid or hollow manufactured plastic lumber product of square,
rectangular, round, or other geometric cross section that shows viscoelastic behavior.
The test specimens are whole “as manufactured” pieces without any altering or machining of surfaces beyond cutting to length.
As such, this is a test method for evaluating the properties of plastic lumber as a product and not a material property test method.
Flexural strength cannot be determined for those products that do not break or that do not fail in the extreme outer fiber.
Test Method A, designed principally for products in the flat or “plank” position.
Test Method B, designed principally for those products in the edgewise or “joist” position.
Plastic lumber currently is produced using several different plastic manufacturing processes.
These processes utilize a number of diverse plastic resin material systems that include fillers, fiber reinforcements, and other chemical additives.
The test methods are applicable to plastic lumber products where the plastic resin is the continuous phase, regardless of its manufacturing process, type or weight
percentage of plastic resin utilized, type or weight percentage of fillers utilized, type or weight percentage of reinforcements utilized, and type or weight percentage
of other chemical additives.
Alternative to a single resin material system, diverse and multiple combinations of both virgin and recycled thermoplastic material systems are permitted in the
manufacture of plastic lumber products.
Diverse types and combinations of inorganic and organic filler systems are permitted in the manufacturing of plastic lumber products.
Inorganic fillers include such materials as talc, mica, silica, wollastonite, calcium carbonate, and so forth.
Organic fillers include lignocellulosic materials made or derived from wood, wood flour, flax shive, rice hulls, wheat straw, and combinations thereof.
Fiber reinforcements used in plastic lumber include manufactured materials such as fiberglass (chopped or continuous), carbon, aramid and other polymerics; or
lignocellulosic-based fibers such as flax, jute, kenaf, and hemp.
A wide variety of chemical additives are added to plastic lumber formulations to serve numerous different purposes.
NOTE —There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
ASTM D6109 / Significance and Use
Flexural properties determined by these test methods are especially useful for research and development, quality control, acceptance or rejection under
specifications, and special purposes.
Specimen depth, temperature, atmospheric conditions, and the difference in rate of straining specified in Test Methods A and B are capable of influencing
flexural property results.
ASTM D6109 / Apparatus
Testing Machine—A properly calibrated testing machine that is capable of operation at a constant rate of motion of the movable head and has the accuracy of
61 % of maximum load expected to be measured.
It shall be equipped with a deflection measuring device.
The stiffness of the testing machine shall be such that the total elastic deformation of the system does not exceed 1 % of the total deflection of the test specimen
during testing, or appropriate corrections shall be made.
The load indication mechanism shall be essentially free from inertial lag at the crosshead rate used.
The accuracy of the testing machine shall be verified in accordance with Practice ASTM E4.
Loading Noses and Supports—The loading noses and supports shall have cylindrical surfaces. In order to avoid excessive indentation, of the failure due to stress
concentration directly under the loading noses, the radius or noses and supports shall be at least 0.5 in. (12.7 mm) for all specimens.
If significant indentation or compressive failure occurs or is observed at the point where the loading noses contact the specimen, then the radius of the loading noses
shall be increased up to 1.5 times the specimen depth
ASTM D6109 / Summary of Test Method
Aspecimen of rectangular cross section is tested in flexure as a beam either in a flat, or “plank,” mode (Method A) or edgewise, or “joist,” mode (Method B)
as follows:
The beam rests on two supports and is loaded at two points (by means of two loading noses), each an equal distance from the adjacent support point.
The distance between the loading noses (that is, the load span) is one-third of the support span
*** Before conducting ASTM D6109 , it is important to read the entire specification. Standards can be obtained from appropriate standard authorities.
***PARSROS offers several types of grips and fixtures which will enable you to perform a variety of tests
that are accurate and repeatable.
Reviews (0)
Be the first to review “ASTM D6109 Test Fixture”
You must be logged in to post a review.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Please Contact with our engineers so that we can find and offer Best Universal Tensile Test Machines , Grips , Jaws and Other Accessories for your operations





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.